If your ear becomes blocked with wax and/or dead skin this is called wax impaction. This may cause one or more of the following symptoms: Dizziness, ear ache, fullness in the ear, a sensation the ear is plugged, partial hearing loss (which may be progressive Tinnitus), ringing, noises in the ear, itching, bad smell, or discharge. At Thurles Family Practice, we remove impacted ear wax via endoscopic micro suction.
Although there are a number of methods used to remove ear wax, we recommend micro suction.
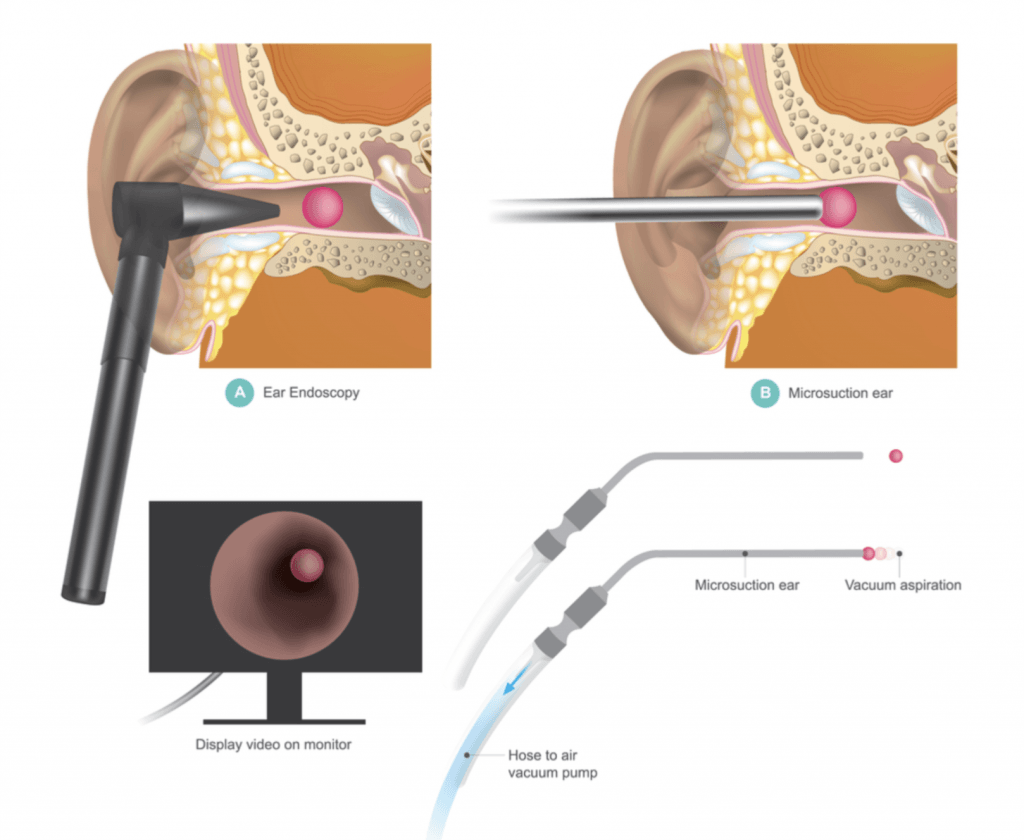
How Does Ear Wax Removal via Endoscopic Micro Suction Work?
- Mild suction is used to bring the wax out, getting away from water which can occasionally send the ear into an overproduction of wax for certain individuals.
- This method is clean, safe & efficient.
- It is less invasive than water irrigation & generally more comfortable.
- After we have removed the wax from your ear, we go back to the endoscope and show you your eardrum intact and healthy.
- If any outer or middle ear pathologies are uncovered during any of the procedures outlined above, photo & video evidence will be sent to your GP for further investigation.
How much does Ear Wax Removal via Endoscopic Micro Suction cost?
Endoscopic Micro Suction on one ear – €50
Endoscopic Micro Suction on both ears – €80
Effects of Impacted Ear Wax
Hearing loss can often be attributed to a build-up of earwax that has accumulated over time.
We see this quite frequently in patients who have been using small tipped objects like cotton buds to “clean their ears”.
A (sometimes) simple solution to hearing loss that can be overlooked is this excess build-up of wax that causes a blockage in the ear canal.
Ear wax is healthy in normal amounts and serves as a self-cleaning agent with protective, lubricating, and antibacterial properties. When there is an absence of earwax this can result in dry, itchy ears.
A normally functioning ear is self-cleaning, with old earwax constantly being transported out of the ear, assisted by chewing and jaw motion, from the ear canal to the ear opening where it usually dries, flakes, and falls out.
However, a small ear canal or downward sloping ear canal can affect the natural migration of earwax and skin out of the ear and result in a blocked ear.

